How Ménière’s Disease Occurs
Ménière ‘s disease is a syndrome that affects the inner ear. It develops due to an increase in endolymph in the labyrinth or an inflammation of the same. This disease is characterized by episodes of vertigo, which are often accompanied by tinnitus (ringing in the ears) and hearing loss. On the other hand, hearing loss is fluctuating and evolves over the years to irreversible hearing loss or deafness.
Mérière’s disease was described by Prosper Ménière, a French physician, in 1861. The doctor pointed out for the first time a lesion in the inner ear as the cause of a vertiginous crisis, that is to say, of clear labyrinthine etiology. Usually this disease affects only one ear. It can occur at any age, but it is more prevalent in adults between 40 and 60 years of age.
The labyrinth
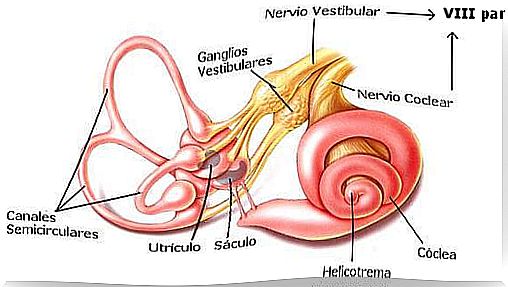
The labyrinth is an organ that contains, in turn, the organs of balance and hearing. Among the first we find the semicircular canals and the otolithic organs. As for the organs of hearing, we can mention the cochlea.
The labyrinth is divided into two sections: the bone labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. The membranous labyrinth is filled with endolymphatic fluid. When the body moves, this fluid stimulates the nerve receptors found in the organs of balance.
These receptors send signals to the brain about the position and movement of the body. In the cochlea, endolymphatic fluid is compressed in response to sound vibrations. This fact causes sensory cells to stimulate and send signals to the brain.
Symptoms of Ménière’s disease
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, the accumulation of endolymphatic fluid is responsible for the development of this disease. The labyrinth interferes with normal hearing and balance signals from the inner ear to the brain. When it fills with fluid is when symptoms such as vertigo can appear.
Attacks or episodes of this disease usually begin without warning. In addition, they can appear from once a year to once a day. Like the frequency, the severity of each episode can vary. The four main symptoms of this disease are as follows:
- Pressure in the ear.
- Tinnitus or ringing in the ear.
- Variable hearing loss or hearing loss.
- Vertigo or dizziness: Vertigo is the symptom that causes the most problems. The patient feels as if he is spinning or as if the world is spinning around him.
With vertigo and dizziness, the patient may also experience nausea, vomiting, and have severe sweating. In addition, they can lose their balance from 20 minutes to 24 hours. Other symptoms associated with Ménière’s disease are:
- Diarrhea.
- Headache.
- Nystagmus or uncontrolled eye movement.
What Causes Disease?

Today there are no definitive answers to clarify what exactly happens for Ménière’s disease to develop. Some scientists think that it is due to a series of vasoconstrictions in a similar way to the case of patients who suffer from migraines.
Other experts have the theory that it may be the result of a viral infection, allergies, or autoimmune reactions. In addition, this disease usually runs in families, so the genetic component could play a role in the appearance of the syndrome.
Although we cannot speak of exact causes, we can speak of certain risk factors that increase the possibility of the appearance of the disease. For example, alcohol consumption, certain allergies or smoking are some of these factors.
Treatment of Ménière’s disease
For the treatment of this syndrome, drugs capable of lowering the endolymphatic pressure of the inner ear are usually used. An example of these drugs is the diuretic family. In addition to the administration of these drugs, salt intake should be decreased.
On the other hand, if there is a respiratory infection, allergy or sinusitis, treatments with anti-inflammatory or histamines are usually recommended. To treat vertigo, antivertiginous drugs such as betahistine are given.
In the most serious cases, surgery of the semicircular canals, the vestibular nerve or labyrinthectomy is used. This type of treatment can affect the normal sensation of balance of the patient, worsening their quality of life.