Bacterial Resistance: What You Can Do To Combat It
Bacterial resistance is increasing at a rapid rate. This is mainly due to ineffective infection prevention and inappropriate use of antibiotics.
Bacterial resistance is one of the most worrying problems in the world today. What has been found in recent years is that infections quickly become resistant to antibiotic treatments. This happens at an ever-increasing rate.
Bacterial resistance is estimated to be increasing exponentially. This is largely due to the misuse of antibiotics, which are sometimes overused and other times irrelevant. We have reached a point where some of the treatments against bacteria are becoming ineffective.
This situation is very dangerous, since we are increasingly defenseless against various infectious diseases. Individual, collective and governmental action is required to prevent the problem from getting worse.
What is bacterial resistance?
Bacterial resistance is the mechanism by which bacteria manage to reduce the action of the agents that attack them. It is a process of natural selection and genetic adaptation, by which these microorganisms manage to overcome drugs.
Bacterial resistance occurs when the antibacterial concentration is four times less than the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC). In other words, when the bacteria have four times the possibility of neutralizing their attacker.
Currently, the speed with which new resistant organisms emerge is greater than the speed with which new antibiotics are designed . We therefore have a deficit that continues to grow and that leaves us in a compromising situation in the face of infectious diseases.
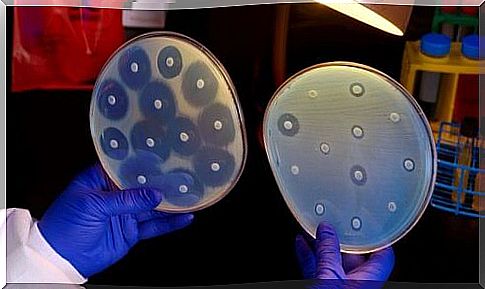
Types and mechanisms of resistance
There are basically two types of bacterial resistance. One is natural, that is, it is part of the very nature of the bacteria. The other is acquired and occurs when genetic mutations occur to repel antibiotic substances. Such mutations are transmitted to other bacteria, even other species.
There are several mechanisms of bacterial resistance:
- The first is the active expulsion of the antimicrobial, which works as a kind of ejector pump.
- The second mechanism is the reduction of the permeability of the bacterial wall, that is, the increase of the access barriers for the antimicrobial.
- The third mechanism is the production of enzymes that render the antibiotic inactive. This means that they inhibit the normal action of the drug, rendering it ineffective.
Strategies to prevent bacterial resistance
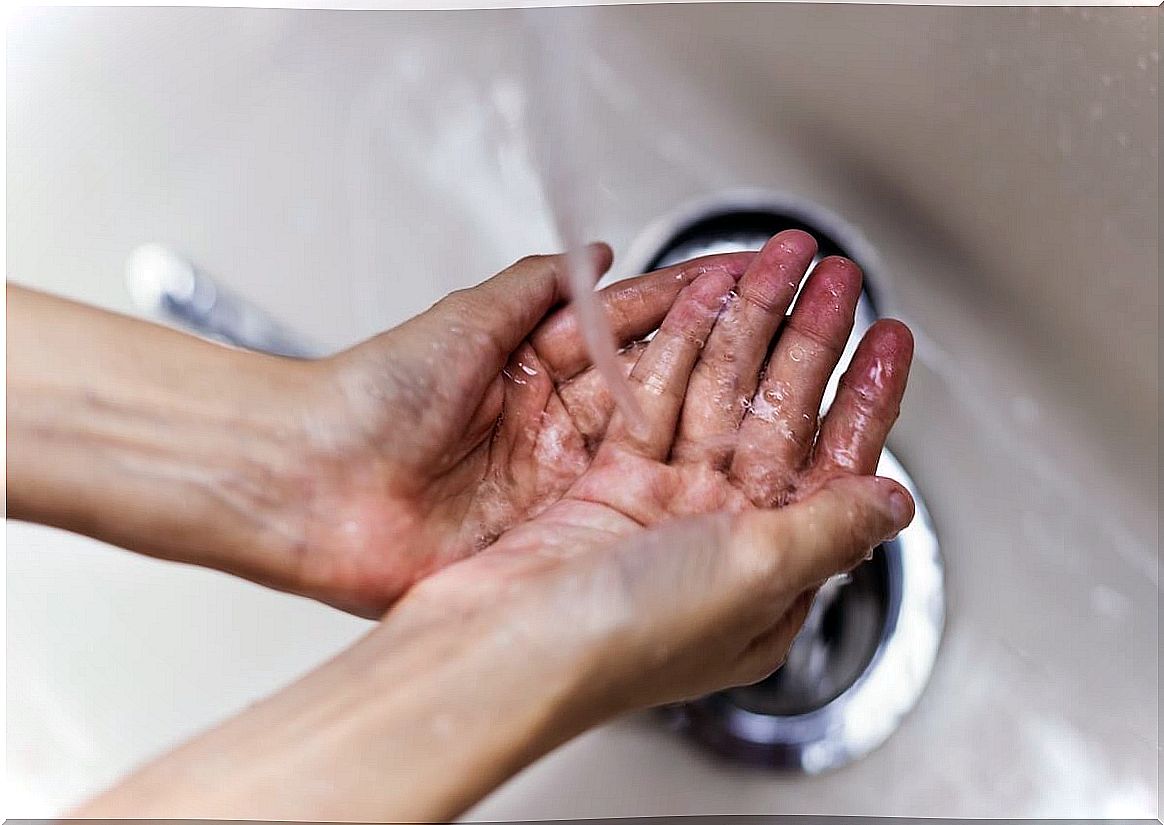
The first strategy to avoid bacterial resistance is to prevent infection. This is achieved, to a large extent, with basic actions such as frequent hand washing, hygienically cooking food, avoiding contact with infected people, having safe sex, and keeping vaccinations up to date.
At this point it is important to point out the importance of a hygienic kitchen. The World Health Organization (WHO) points out five keys:
1) Keep kitchen spaces and elements clean
2) Separate raw food from cooked
3) Cook thoroughly
4) Preserve food at the right temperature
5) Use clean water and uncontaminated raw material
Likewise, it is very important that people take antibiotics only when the doctor prescribes them, avoiding self-medication. The professional’s instructions regarding schedules and dosage must be strictly followed.
You should not stop treatment even if you feel better. If you do not take the prescribed amount of drugs, you run the risk of developing more resistant bacteria.

Other control measures
It is indicated that workers in the agricultural sector use antibiotics with animals only under strict supervision of the veterinarian. The inappropriate use of these drugs in agriculture or livestock is one of the main causes of bacterial resistance. It spreads to the environment and to humans through the food chain.
Health personnel should also take extreme control measures against this issue. It has been found that 50% of antibiotics are prescribed for viral diseases, despite the fact that this is not indicated. Antibiotics should only be prescribed if it is certain that they are absolutely necessary.
Government authorities and independent institutions must remain vigilant to any outbreak of infection and determine as soon as possible if it is resistant to antibiotics. It is also essential that they inform and educate citizens to prevent infectious diseases.
It is necessary that researchers and the pharmaceutical industry join forces to intensify studies on this issue. The whole world should support research in this regard, since a large part of our well-being and our future depends on it.