Fat Lumps On The Back: What Are They Caused By?
The discovery of fat lumps on the back causes concern in the person who finds them. Sometimes not just one is produced, but is accompanied by other smaller lumps, and that alerts even more.
However, it is important to establish a differential diagnosis of the lesion. That is, although it looks like a fat lump, it may be another pathology, such as a sebaceous cyst or a boil.
Although it is true that fat is the most frequent cause of this symptom, it does not hurt to make a medical consultation to establish what it really is. Sometimes a clinical examination alone is sufficient to determine the origin of the lump, without the need for further studies.
Specifically, a buildup of fat on the skin is called a lipoma. The name refers to its conformation, which consists of adipocytes – cells with lipids.
Lipomas are not malignant, and are generally limited to a size that does not affect other structures in the body. However, there are entities such as the giant lipoma and internal lipomas, which can lead to unexpected complications, to the point of interrupting the functioning of other organs.
Differential Diagnosis for Fat Lumps
As we anticipated, the existence of a lump of fat on the back requires a differential diagnosis. We have to assess whether we are dealing with a lipoma or another skin lesion with similar symptoms. Next, we detail the three most frequent ones.
1. Lipoma
This is the classic fat lump. Its growth is slow, progressive, and becomes evident when the patient discovers it, sometimes by accident. It is not painful and reaches a point of equilibrium where it stops growing – except for the exceptions we mentioned. If it is small, doctors usually recommend doing nothing. If it is large or aesthetically uncomfortable, it is removed with local surgery.
2. Boil
A boil is an infection of the hair follicle. It can appear on the back, especially in the lower area, where there is more presence of hairs. Sometimes it hurts, and sometimes it doesn’t. The pain is usually associated with an infection that is added.
If there is this complication, pus appears, which makes pressure to come out; this is a difference with lipoma, which does not present secretions. Treatment of a boil consists of antibiotics if there is infection, drainage if there is pus, and local washes with antiseptics.
3. Sebaceous cyst
This lesion is very similar to lipomas in its composition, since it has fat inside. The histological difference is that it has a cyst lining and some fluid inside. It almost never hurts, but it can become infected, such as a boil.
It is mobile to the touch and even sinks a little under pressure. Like a lipoma, treatment is based on its size and discomfort; If it is decided to remove it, a local surgery is done.
Symptoms and risk factors
The fat lump or lipoma is common on the back, although it can also appear on the upper limbs and neck. It is rarer to observe them in the lower limbs.
When touched, the lipoma has a certain mobility and softness. Under pressure it may sink minimally, but it is not liquid like a cyst, so it offers some resistance to palpation. For the doctor it is usually easy to identify them, since the touch is characteristic.
The size of the fat lumps does not exceed 4-5 centimeters for the most part. If it is larger, we are already talking about a giant lipoma, which is an entity in itself. It requires a different approach because it penetrates deeper structures and its removal is not as easy as in other cases.
The origin of lipomas is not known with certainty. It is assumed that there is some kind of genetic link, since fat lumps appear repeatedly in family groups with this tendency. But there are no conclusive studies on this.
Regarding age, the most affected group is that of adults, between 30 and 60 years old. There is also no clear information on why it is distributed this way.
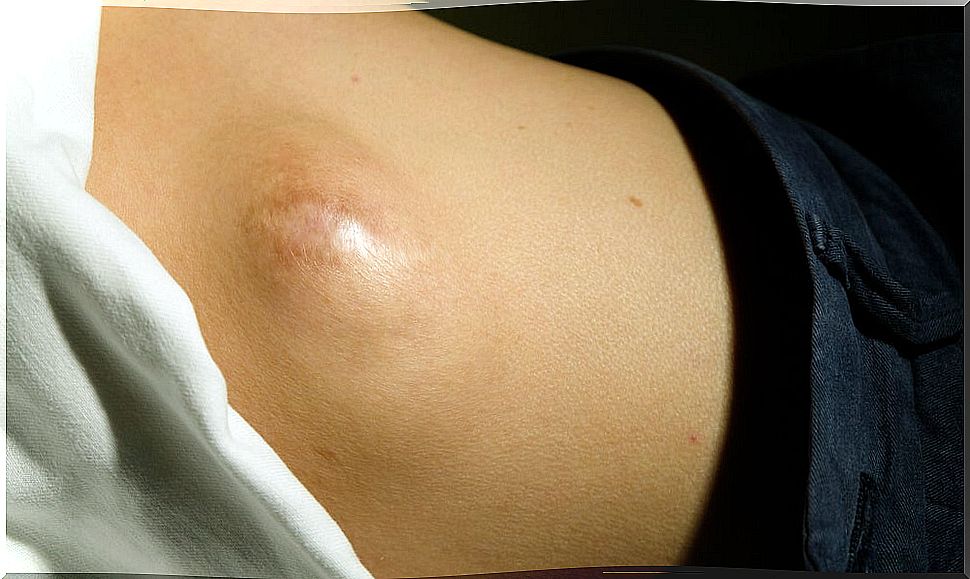
When to see if I have a fat lump on my back?
The consultation should be imposed when detecting a lump of fat in the back to perform the differential diagnosis. It will be the medical professional who knows how to quickly distinguish if it is a lipoma or another entity. Similarly, it will order complementary methods or not based on gravity.
Some added symptoms warn of the need to consult more quickly, such as:
- Increase in lump size
- Presence of pus that drains out
- Hardening of the suspected lipoma with loss of mobility and softness
- Swollen glands near the area
Pay attention to fat lumps
Although they are benign, lipomas require attention. It is better to consult and achieve a differential diagnosis than to remain in doubt. Much more so if symptoms are associated that produce the suspicion of infection, compression of neighboring structures or enlargement of size.