Can Gastric Ulcers Be Prevented?
Gastroduodenal ulcer is a fairly common entity and, in addition, a high recurrence rate of the disorder is observed among patients. Therefore, being able to prevent gastric ulcers is an opportunity that must be taken advantage of.
A low percentage of patients with the disease can present as complications bleeding and perforation, with the consequent risk of life. This is not a minor issue.
What are gastric ulcers?
Gastric ulcers are defects or sores in the inner lining of the stomach or duodenum (portion of the small intestine that follows the stomach). They are also often called peptic ulcers .
They develop and persist thanks to the acid activity of gastric juice. The disease is associated with two main factors: Helicobacter pylori bacterial infection and the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
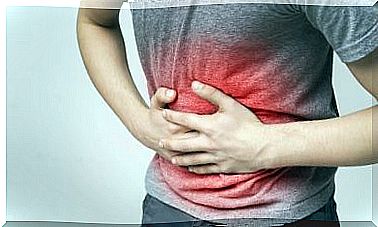
Most people who have a gastric ulcer will be asymptomatic or only have dyspepsia:
- Pain in the pit of the stomach.
- Burning or heartburn.
- Food intolerance with belching and bloating.
- Nausea and vomiting
Complications of gastric ulcer include bleeding, penetration, perforation, and obstruction of the gastric outlet. They have decreased compared to previous decades, thanks to the identification and treatment of H. pylori .
What Factors Make Gastric Ulcers More Likely?
One of the determining factors is gastric infection by Helicobacter pylori . Between 85% and 100% of patients with gastroduodenal ulcers are positive for the presence of the bacteria in the stomach or duodenum.
Similarly, the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, indomethacin, diclofenac, piroxicam, and naproxen, along with other drugs, such as cigarettes and alcohol, are risky practices. The problem increases progressively with more years of employment.
It is also known that there is a family predisposition to the presentation of ulcers. This genetics must be strengthened with habits to end in disease, as happens with the intake of certain foods and beverages that can cause an upset stomach. Eating a healthy diet with lots of fruits, vegetables, and fiber can lower your risk for them.
The role of stress in ulcer formation is controversial. There is some evidence that it can contribute to its development, as well as partial healing and increased recurrence.
How to prevent gastric ulcers?
To prevent gastric ulcers, we leave you here some recommendations that you can follow and that are framed in the context of healthy habits and medical therapeutics with scientific evidence:
- Avoid the use of aspirin whenever possible. In particular, its indication should be carefully evaluated in patients with a history of gastric ulcer. In the same way, the smallest possible doses should be used, accompanying them with meals. In case of requiring the use of analgesics, paracetamol is preferable.
- For patients who have a history of ulcers and must continue with aspirin or another NSAID, concomitant treatment with a proton pump inhibitor (eg omeprazole) is usually recommended for as long as they are used.
- Eradicate H. pylori infection with antibiotics. Multiple antibiotics have been tested and many of them failed to clear the infection. The selected treatment regimen must consider the local resistance patterns of the bacteria. One of the regimens used is the combination of clarithromycin and amoxicillin for 14 days.
- Avoid cigarettes and limit the amount of alcohol.
- Change your diet: avoid chocolate, fatty foods, fried foods, coffee, citrus fruits and highly seasoned foods. Although it is known that they are not a direct cause of gastric ulcer, they can make it worse, so it is always suggested to reduce their consumption.
- Avoid being overweight.

Preventive measures are important to avoid recurrence
Those patients who suffered gastric ulcers before will benefit from most of the prevention measures already recommended. Above all, the emphasis should be on avoiding the use of NSAIDs and smoking.
In addition, on many occasions, eradication of H. pylori will be evaluated with a doctor. This is not something that can be decided by the patient alone. Complementary methods must be carried out to corroborate the existence of the bacterium, as well as its antibiotic resistance. Once this process has been completed, the action protocol will be established.
Healthy habits, stress reduction and dietary measures, although not causal factors, can improve symptoms or prevent the worsening of dyspepsia. There are no magic formulas for this prevention, although it does require commitment and persistence in the changes that are applied.